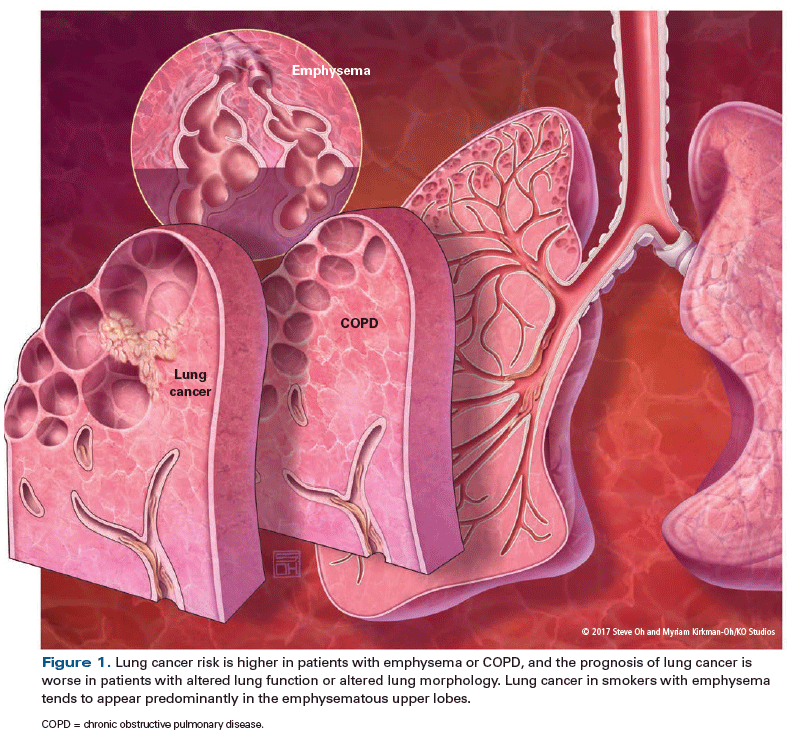
Emphysema can be defined as having a loss of lung elasticity permanent enlargement of the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles and destruction of the alveolar walls.
Hanging ends of alveolar walls emphysema.
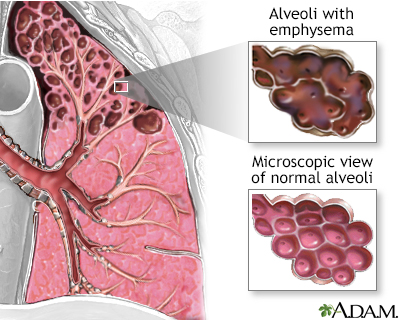
Emphysema is a condition that involves damage to the walls of the air sacs alveoli of the lung.
Type 1 squamous alveolar epithelial cells.
Alveoli are small thin walled very fragile air sacs located in clusters at the end of the bronchial tubes deep inside the lungs.
Inhaled air becomes trapped harder to exhale.
It typically affects the upper lobes first and most profoundly.
Results from pathological destruction of the alveolar walls and septae from long term exposure to irritants.
The one cell thick walls of the alveoli are composed of two distal airway epithelium cell types pneumocytes 7.
Signs and symptoms include minimal coughing and barreled chest.
Pulmonary emphysema defines permanent dilatation of airspaces due to destruction of alveolar walls.
Bronchitis is an inflammation and swelling of the bronchial walls.
It can be classified under the umbrella term chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder copd 1.
They often occur together.
It is one end of the spectrum of copd resulting from the smoking of tobacco.
In 1984 the division of lung disease at the nhlbi funded a workshop which led to what is still the most recent official definition of emphysema i e a condition of the lung characterized by abnormal permanent enlargement of airspaces distal to the terminal bronchiole accompanied by the destruction of their walls and without obvious fibrosis 1.
12 distal airspace enlargement with alveolar destruction reduces maximal expiratory airflow by decreasing the lung elastic recoil.
Emphysema destruction of alveolar alveolar capillary walls narrowed and tortuous small airways leads to large permanently inflated alveolar spaces.
Later stages of emphysema adjacent damaged alveoli forming even larger air spaces.
Consequences of alveolar destruction.
Pneumothorax occurs when pleural membrane surrounding large.
Emphysema also called pulmonary emphysema condition characterized by widespread destruction of the gas exchanging tissues of the lungs resulting in abnormally large air spaces lungs affected by emphysema show loss of alveolar walls and destruction of alveolar capillaries as a result the surface available for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between inhaled air and blood traversing.
There are three types of emphysema.
A person with chronic bronchitis typically has a daily cough with phlegm that lasts for months at a time over several years.
Loss of surface area for gas exchange.