True the oldest sedimentary rock strata are exposed along the axial parts of deeply eroded anticlines.
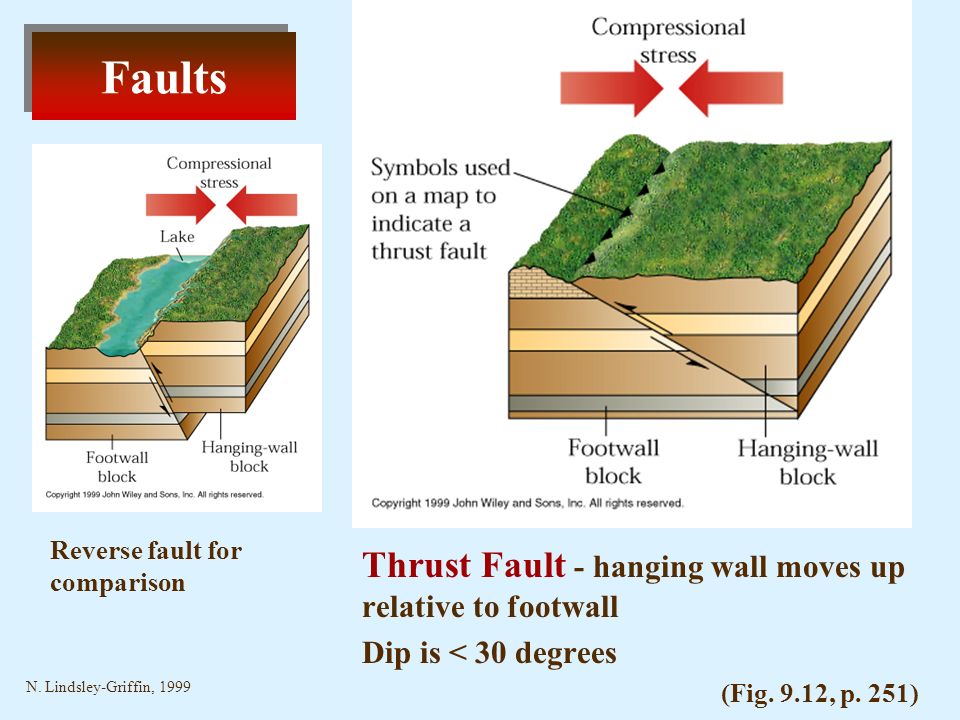
Hanging wall moves up relative to footwall.
The motion of the crustal blocks is referred to as strike slip.
Reverse faults indicate compressive shortening of the crust.
The hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall.
The dip of a reverse fault is relatively steep greater than 45.
A fault in which the hanging wall moves up relative to the foot wall.
In a reverse fault the hanging wall block moves up relative to the footwall block.
Opposing forces cause rock to break and move horizontally.
A fault in which the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall.
The hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall.
A fault that does not break the ground surface.
Thrust faults low angle fault hanging wall moves up relative to footwall.
When movement along a fault is the reverse of what you would expect with normal gravity we call them reverse faults.
The terminology of normal and reverse comes from coal mining in england where normal faults are the most common.
Reverse faults high angle fault hanging wall moves up relative to footwall.
Normal fault s are common.
In fault normal dip slip faults are produced by vertical compression as earth s crust lengthens.
When the hanging wall moves up in relative to the footwall it is called a fault.
Strike slip faults high angle fault two sides move pass each other horizontally.
The footwall moves down relative to the hanging wall.
These usually happen when tectonic forces causes compression that pushes rocks together.
In thrust or reverse faults the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall and in strike slip faults it moves horizontally relative to the footwall.
They bound many of the mountain ranges of the world and many of the rift valleys found along spreading margins.
Strike slip faults have a different type of movement than normal and reverse faults.
The hanging wall slides down relative to the footwall.
A reverse fault is the opposite of a normal fault the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall.
When rock layers are squeezed together and pushed upward.
The crust experiences extension.
Faults occur when opposing forces causes rock to break and move horizontally.